Balance Improvement Calculator
Based on a 2023 Journal of Sports Science study showing a 27% improvement in balance after 6 weeks of Pilates practice. This tool estimates your potential progress based on your practice frequency.
Your Balance Progress
After 4 weeks
After 6 weeks
Struggling with wobble, weak core, or just can’t feel your muscles working together? You’re not alone. Many people experience poor muscle control, which makes everyday tasks feel harder than they should. The good news? Pilates offers a low‑impact way to tighten that loose connection between brain and body. Below is a practical guide that shows exactly how Pilates can sharpen muscle control and give you rock‑solid stability.
Key Takeaways
- Pilates targets deep stabilizing muscles, not just the big movers.
- Regular practice improves proprioception - the body’s internal GPS.
- Core stability gained from Pilates reduces injury risk in daily life.
- Even a 15‑minute routine can deliver noticeable gains.
- Combine Pilates with mindful breathing for maximum effect.
What is Pilates?
Pilates is a low‑impact exercise system that emphasizes precise, controlled movements, breath work, and a strong mind‑body connection. Developed by Joseph Pilates in the early 20th century, the method was originally called “Contrology” because it teaches practitioners to engage the smallest stabilizing muscles before the larger ones. Modern classes can be done on a mat, a reformer machine, or even a simple chair - making the practice adaptable for all fitness levels.
How Pilates Boosts Muscle Control
Muscle control isn’t just about strength; it’s about coordination, timing, and awareness. Pilates tackles all three by teaching you to activate the deep core and postural muscles first. When you learn to “turn on” these tiny fibers, the larger muscles follow, resulting in smoother, more efficient movement.
Research from the Journal of Sports Science (2023) showed that a six‑week Pilates program improved participants’ ability to maintain balance on one leg by 27 % compared with a control group doing standard stretching. The study attributed the gains to enhanced proprioception - the body’s sense of where its parts are in space.
Core Stability Explained
At the heart of Pilates is core stability. This isn’t just the six‑pack; it’s a deep muscular “corset” made up of the transverse abdominis, multifidus, diaphragm, and pelvic floor. When these muscles contract together, they create a stable trunk that protects the spine and supports every limb movement.
Think of it like a solid foundation for a house. If the foundation shifts, the entire structure wobbles. Strengthening the core gives you a firm base, so your arms, legs, and even your head can move confidently without wobbling.
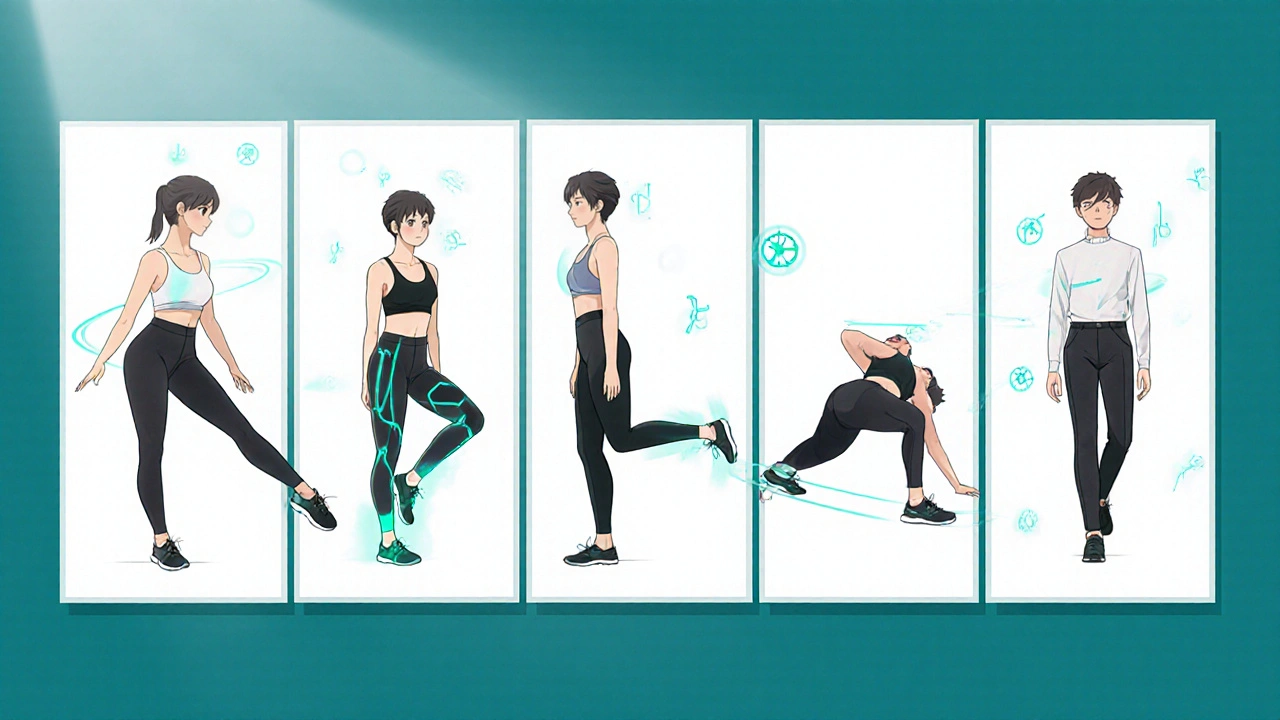

Proprioception and Balance
Proprioception - often called the body’s internal GPS - tells your brain where each joint is without you having to look. Pilates drills constantly challenge this sense by forcing you to hold positions, shift weight, and transition smoothly between moves.
One classic move, the Hundred, requires you to lie on your back, lift your head and shoulders, and pump your arms while maintaining stable hips. This simple exercise trains the nervous system to stay aware of subtle changes in posture, which translates to better balance on stairs, in the kitchen, or while playing with kids.
Best Beginner Pilates Moves for Muscle Control
Below are five beginner‑friendly exercises that directly target muscle control and stability. Perform each for 8‑10 breaths, focusing on precise form.
- Pelvic Tilt: Lie on your back, knees bent, feet flat. Gently tilt your pelvis upward, flattening the lower back against the floor. This activates the transverse abdominis.
- Single‑Leg Stretch: On a Pilates mat, pull one knee into your chest while extending the opposite leg, keeping the low back pressed into the mat. Switch sides, maintaining a steady breath.
- Roll‑Up: Sit tall, legs straight, arms reaching forward. Slowly roll down one vertebra at a time, then reverse the motion, stacking the spine back up. This builds spinal articulation and abdominal control.
- Side‑Plank (Modified): From a forearm plank, shift weight onto one forearm, stack the feet, and lift the hips. Hold for a few breaths, then switch. This challenges lateral core stability and shoulder endurance.
- Standing Balance: Stand tall, shift weight onto one foot, and lift the opposite knee to hip height. Keep a soft bend in the standing leg. Extend arms forward for extra challenge.
Integrating Pilates into Your Routine
Consistency beats intensity when it comes to muscle control. Here’s a simple weekly schedule you can follow:
- Monday & Thursday - 20‑minute mat session: Focus on core activation (Pelvic Tilt, Roll‑Up, Hundred).
- Tuesday - 10‑minute balance drill: Standing Balance and single‑leg work.
- Saturday - 30‑minute full‑body flow: Combine all moves with a gentle breathing technique (inhale through the nose, exhale through the mouth while keeping the core engaged).
Even on busy days, a quick 5‑minute “micro‑session” of Pelvic Tilts and breathing can reset posture and reinforce neural pathways.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When you’re new, it’s easy to slip into habits that actually diminish the benefits.
- Holding your breath: Pilates relies on breath to cue muscle activation. Practice the 1‑2‑3‑4 inhale‑exhale rhythm.
- Relying on momentum: Fast, jerky movements bypass the deep stabilizers. Slow down and feel each muscle engage.
- Neglecting spinal alignment: A rounded back or over‑arched spine puts stress on the vertebrae. Keep the neutral spine “long” throughout.
- Skipping the warm‑up: A few gentle cat‑cow stretches prime the spine for safe movement.
Comparison: Pilates vs Traditional Strength Training
| Aspect | Pilates | Strength Training |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Improved muscle control & core stability | Increase maximal force output |
| Typical Load | Bodyweight or light resistance | Heavy weights, barbells |
| Impact on Joints | Low impact, joint‑friendly | Higher impact, potential stress |
| Focus on Mind‑Body Connection | High (breathing, precision) | Variable, often lower |
| Benefit for Balance | Significant, via proprioceptive drills | Limited, unless functional training |
Quick FAQ
Can Pilates help with lower back pain?
Yes. By strengthening the deep core muscles and improving spinal alignment, Pilates often reduces pressure on lumbar discs, leading to less pain for many sufferers.
How often should I practice to see results?
Consistency beats intensity. Aim for 3-4 short sessions per week (15-20 minutes each). Noticeable improvements in balance and muscle control often appear after 4-6 weeks.
Do I need special equipment?
A good Pilates mat and a sturdy surface are enough for beginners. As you progress, you might add a reformer or resistance bands, but they’re optional.
Is Pilates suitable for athletes?
Absolutely. Many elite athletes use Pilates to fine‑tune proprioception, prevent injuries, and improve cross‑training performance.
Can I combine Pilates with yoga?
Yes, the two complement each other well. Yoga adds flexibility and mindfulness, while Pilates supplies core strength and precise control.
Whether you’re recovering from an injury, looking to sharpen athletic performance, or simply want to stand taller without feeling wobbly, Pilates offers a science‑backed path to better muscle control and stability. Start with the basics, stay consistent, and watch your confidence grow as your body learns to move with purpose.


Andrew Hernandez
October 20, 2025 AT 22:18Pilates tones core efficiently.
Mahesh Upadhyay
October 23, 2025 AT 05:51If you keep ignoring your wobble, you’re basically signing a contract with injury.
Pilates is the only antidote that forces you to respect your own body.
Stop making excuses and engage the deep stabilizers now.
Rajesh Myadam
October 25, 2025 AT 13:24I get why many feel stuck when their core feels like a loose rope. The guide does a solid job breaking down why the transverse abdominis matters. Those pelvic tilt and roll‑up drills are perfect starters. Consistency is key-just a few minutes each day builds neural pathways. Keep breathing through each move and you’ll notice steadier balance in everyday tasks.
Natalie Morgan
October 27, 2025 AT 19:58I noticed the Hundred really sharpens proprioception especially when you sync breath to movement.
Kate McKay
October 30, 2025 AT 03:31Starting a Pilates routine can feel intimidating, but think of it as learning a new language for your body. The first step is to treat each breath as a cue, not just a background noise. When you inhale, you create space; when you exhale, you draw the deep core inward. This simple pattern translates to better spinal alignment during the Pelvic Tilt and Roll‑Up. As you repeat the moves, your nervous system begins to map the correct activation patterns. Over a few weeks you’ll notice that standing on one leg feels steadier without consciously trying. The Standing Balance exercise becomes less of a wobble and more of a controlled shift. You’ll also find that everyday activities-carrying groceries, reaching for a high shelf-feel smoother. The magic lies in the cumulative effect of those micro‑sessions you slip into a busy day. Even five minutes of focused breathing and a couple of Pelvic Tilts reset posture. Consistency beats intensity, so aim for short, frequent practice rather than occasional marathon sessions. Listening to your body’s feedback is crucial; if a move feels strained, modify it rather than push through. The core isn’t just for looks; it’s the foundation that protects your spine and enhances athletic performance. For athletes, integrating Pilates can close the gap between strength and agility. For anyone dealing with lower‑back pain, the deep stabilizers offer relief by unloading the lumbar discs. Remember, progress is a series of tiny wins, not a single dramatic breakthrough. Keep a journal of how you feel after each session; patterns will emerge that guide you toward the moves that work best for you. Most importantly, celebrate the moments when you notice less wobble-those are the real results of disciplined practice.
Alex Pegg
October 31, 2025 AT 21:11All that hype ignores the fact that real strength still comes from heavy lifting.
laura wood
November 2, 2025 AT 14:51I understand how frustrating that feeling can be, and it’s encouraging to see you push for better control.
Demetri Huyler
November 4, 2025 AT 08:31While the layperson basks in feel‑good anecdotes, the discerning athlete knows that true functional mastery demands a regimen steeped in biomechanical precision, something Pilates offers when paired with a disciplined mindset-an approach many casual practitioners seem to overlook.
JessicaAnn Sutton
November 6, 2025 AT 02:11It is imperative to acknowledge that the systematic activation of the transverse abdominis, as described, constitutes a scientifically validated method for enhancing postural stability, and any dismissal of this technique as merely trend‑driven is intellectually untenable.
Israel Emory
November 7, 2025 AT 19:51Indeed, the incorporation of deliberate breathwork, consistent spinal articulation, and mindful proprioceptive drills, all of which are emphasized in the routine, serves not only to fortify the deep core muscles, but also to recalibrate the central nervous system, thereby fostering a holistic improvement in balance, coordination, and overall bodily awareness.
Sebastian Green
November 9, 2025 AT 13:31I’ve found that even a brief focus on the Hundred and single‑leg stretch makes my daily posture feel noticeably steadier.